Rooting is a popular choice among advanced Android users, as it grants them complete control and customization over their devices. However, there are valid reasons why Android phones don’t come rooted out of the box, primarily due to security concerns. Here’s a closer look at why rooting is not recommended for everyone:
1. Security Risks

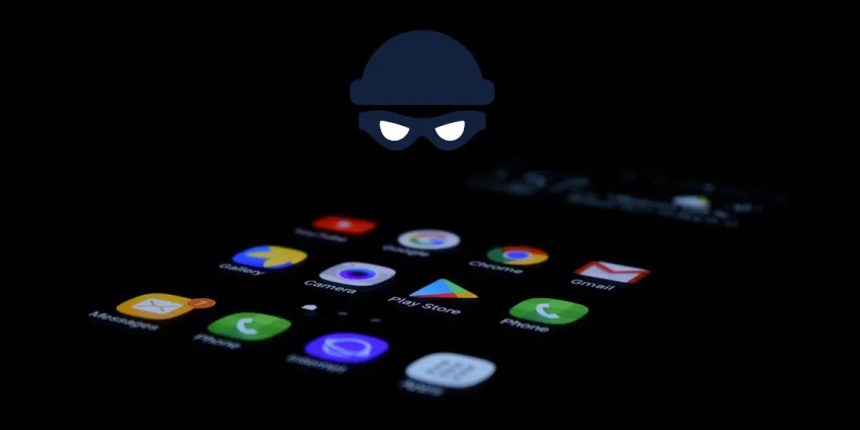
Rooting provides unrestricted access to the operating system, bypassing built-in security measures implemented by the manufacturer and Google. This elevated access level can potentially expose the device to security threats, including malware, unauthorized access, and data breaches. On a non-rooted phone, apps can only perform actions for which they have been granted permission, creating a safer environment. However, on a rooted phone, even a malicious app can wreak havoc by gaining system-level access, compromising sensitive information such as passwords, banking details, and personal photos.
By keeping Android phones unrooted by default, manufacturers prioritize user security and protect inexperienced users from inadvertently exposing themselves to such risks. Non-rooted devices offer a controlled environment where apps operate within predefined permissions, mitigating potential security vulnerabilities.
It’s important to note that rooting can have legitimate uses and benefits for experienced users who understand the risks involved and take necessary precautions. However, for the average user, the added security provided by a non-rooted device outweighs the advantages of rooting.
Remember, these are general considerations, and the decision to root an Android device ultimately lies with the user, taking into account their technical knowledge and willingness to assume the associated risks.
2. To ensure that The System Files Safe

Another type of security rooting could compromise is the security of the security of your Android device’s files on the system. It’s no surprise that system files are the ones that your Android OS is running on. If you erase or lose the most important data file on your smartphone, it may fail, display constant errors, or become stuck in the bootloop.
If your phone is not rooted on a phone that isn’t rooted, your Android file manager application like the Files app from Google isn’t able to access the system file. But, the root file explorers have access to every aspect of your phone including system files. Therefore, in this scenario the risk is not external, such as hackers, but internally for the user’s personal security.
3. Carriers and Manufacturers Care About Branding

A majority of companies and manufacturers use an specific Android Skin to promote branding. With no root access, they are able to retain control over their brand-named elements and offer a consistent user experience, which is aligned with their business objectives. When a device is secured and you have the capability to alter or eliminate these modifications, including the brand-name apps of the manufacturer.
It’s not just the branding they’re after. It’s the value-added products like cloud storage and applications for office suites. This is one way the companies generate revenue after sales.
It’s possible to get rid of bloatware with ADB with no root If you’re after that However, be sure to remove recommended apps and not the ones that are essential.
Another reason that companies do not prefer pre-rooted devices is that it may lead to the creation of more modifications. Once you’ve rooted, the well-known option for advanced users is to install an custom ROM that completely removes the skin of the manufacturer or carrier. It’s not really helping their cause.
4. Google Doesn’t Have Control over the way it advertises

Google earns most of its income through advertising. It has a variety of advertising platforms for businesses to utilize to advertise their products, services and brands, to an larger market. Privacy and security of data are crucial considerations. Google has put in place measures to ensure that it is in compliance with privacy regulations as well as user consent obligations.
To keep its control over its apps, products and ads phones aren’t rooted by default since Google does not want you to eliminate its ads and applications. You can, however, utilize an Android device without Google in case you’re bored of its offerings.
5. A lot of apps don’t work on phones that are Rooted

Many apps recognize a root phone, but they don’t work due to security and privacy concerns. They have policies in place to restrict the use of phones that have certain access levels.
Banking apps are among the most popular examples that won’t function on a rooted device. They contain sensitive financial data, and a device that is rooted could expose them to vulnerabilities. It is possible that you will have issues with Android antivirus applications when you own a phone that has been rooted. The apps consider rooting to be as a security risk for the reasons that we’ve already discussed.
Many games available on the Play Store implement an anti-cheating algorithm that detects and blocks cheating players. These algorithms aren’t a fan of root phones because root users could hack or alter the game, which is unfair to honest gamers.
Another option is streaming apps that provide copyrighted content. A device that is rooted is the potential site for piracy or unauthorised access to content. As such, the majority of streaming apps prohibit use on root devices.
6. OTA Updates Don’t Support Rooted Phones

OTA also known as Over The Air updates bring improvements as well as security patches, bug fixes and other new features to your device without having to manually do anything. If your phone is rooted and this update is installed, it will be affected as your system files could be altered, and these modifications could render the OTA update unusable for the device.
If you attempt to attempt to force the installation of an OTA update to a root device, it can result in system failure. Fortunately, it won’t get to that point since the OTA update is able to detect root access but fails to complete installation.
7. The higher chance of bricking isn’t ideal for a warranty

Bricking happens when your device ceases to function and becomes permanently damaged (known as”hard bricked). This is among the possible consequences of the installation of custom ROMs and could be caused by any error made in the procedure.
If the device becomes bricked because of rooting, makers will probably refuse to offer support or repair under warranty. If they create Android phones that are pre-rooted, they’ll need to fix a large number of broken phones each day adding costs and the labor required to a significant extent and rendering it unattainable.
The art of rooting isn’t for everyone.
In light of the information above You’ll agree that unrooted phones are better for an average user. If root is disabled as a default feature, a user who has no prior knowledge of the device would probably harm their device, and possibly be targeted by hackers.
With the numerous improvements to this version of the Android OS over the years it is possible to argue that rooting isn’t necessary anymore, and not even for the most advanced users. In addition, you can modify the settings of your Android device without root.